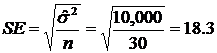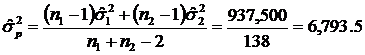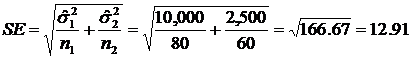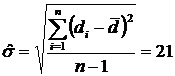The t Tests
Lecture 7
|
The t Distribution
|
|
-
The t-tests are similar to the z-tests
-
However, you assumed you knew the population variance
-
In reality, the variance has to be estimated too!
-
Switch to the t distribution

-
The t-distribution is shorter and fatter because you estimated two parameters, the mean and the variance
-
The Rule of Thumb
-
If the observations are less than 30, then use the t-distribution
-
If the number of observations are equal to or greater than 31, then use the z-distribution as an approximation
-
Example
-
You survey 30 people in Almaty. The average income, 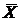 = $600 per month and variance, = $600 per month and variance,  = 10,000 = 10,000
-
Find the 95% Confidence Interval
-
Use an a = 0.05 and df = 30 – 1 = 29
-
Using Excel, = tinv( a, df)
-
t c = 2.04523
-
If this was a normal distribution, then z c = 1.96
-
The standard error (SE) is
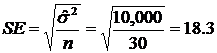
-
-
The 95% Confidence Interval is

-
-
There is a 95% chance that the true population mean lies between [562.5, 637.5]
|
Testing the Means between Two Samples
|
|
-
Testing the Difference of the means of two samples
-
This is more complicated because you are estimating the variance
-
Two methods
-
If the variances are equal, then pool the variances
-
If the variances are unequal, then use a different method to pool the variance
-
Assume the variances are equal
-
Example
-
You survey 80 people at Mega Center
-
The average income is  = $800 per month = $800 per month
-
The estimated variance is  = 10,000 = 10,000
-
You survey 60 people at Thieves’ Market
-
The average income is  = $500 per month = $500 per month
-
The estimated variance is  = 2,500 = 2,500
-
Note – you should test data to determine if data is normally distributed
-
Variance is calculated at

| Variance in Sample 1
|
|
|
(n 1 – 1) 
|
(80 -1)(10,000)
|
790,000
|
| Variance in Sample 2
|
|
|
(n 2 – 1) 
|
(60 – 1)(2,500) |
147,500
|
|
Total Variance |
937,500 |
-
Total degrees of freedom = n 1 – 1 + n 2 – 1 = 80 + 60 – 2 = 138
-
The pooled variance is
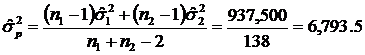
-
The standard error is

-
The t-statistic is

-
If a = 0.05, then the t c = 1.977304
-
The p-value is 5.01 X 10 -15
-
The hypothesis test is

-
Reject the H 0 and conclude the population means are different
-
Can use a Confidence Interval for hypothesis test

-
Assume variances are unequal
-
Same example
-
The  =10,000, n 1 = 80, =10,000, n 1 = 80,  =2,500, and n 2 = 60 =2,500, and n 2 = 60
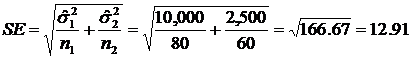
-
However, we have to adjust the degrees of freedom

-
Round the degrees of freedom to 122
-
The t-statistic is

-
Reject the H 0 and conclude the population means are different
|
Difference of Means of Paired Observations
|
|
-
We have observations that are paired
-
Two treatments, A and B
-
Example: Patients are given two types of blood pressure medicine
| Observations |
Treatment A |
Treatment B |
Difference |
| 1 |
64 |
84 |
-20 |
| 2 |
67 |
51 |
16 |
| 3 |
49 |
61 |
-12 |
| . |
. |
. |
. |
| 23 |
72 |
70 |
2 |
-
Calculate the average for the differences, 
-
Calculate the standard deviation of the differences
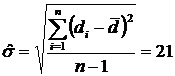
-
The standard error is

-
The hypothesis test is

-
The t-statistic is

-
The a = 0.05, df = 23 – 1 = 22, and t c = tdist( a, df) = 2.034
-
Fail to reject the H 0 and conclude both treatments are similar
-
The paired test is a more powerful test than the other two
-
Contains more information, because you took the extra step of pairing the observations
|